-40%
Detailed classic coal age Lepidodendron scale tree & rarer Stigmaria species !!!
$ 24.28
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
My specimens are genuine and will be delivered with a Certificate of authenticity, age and origin and scientific works copy described this species !I combine shipping costs.
Each item is different, so please wait with payment after purchase -
I will send You a combine invoice.
Usually, it will be cost of shipping the heaviest item.
Specimen:
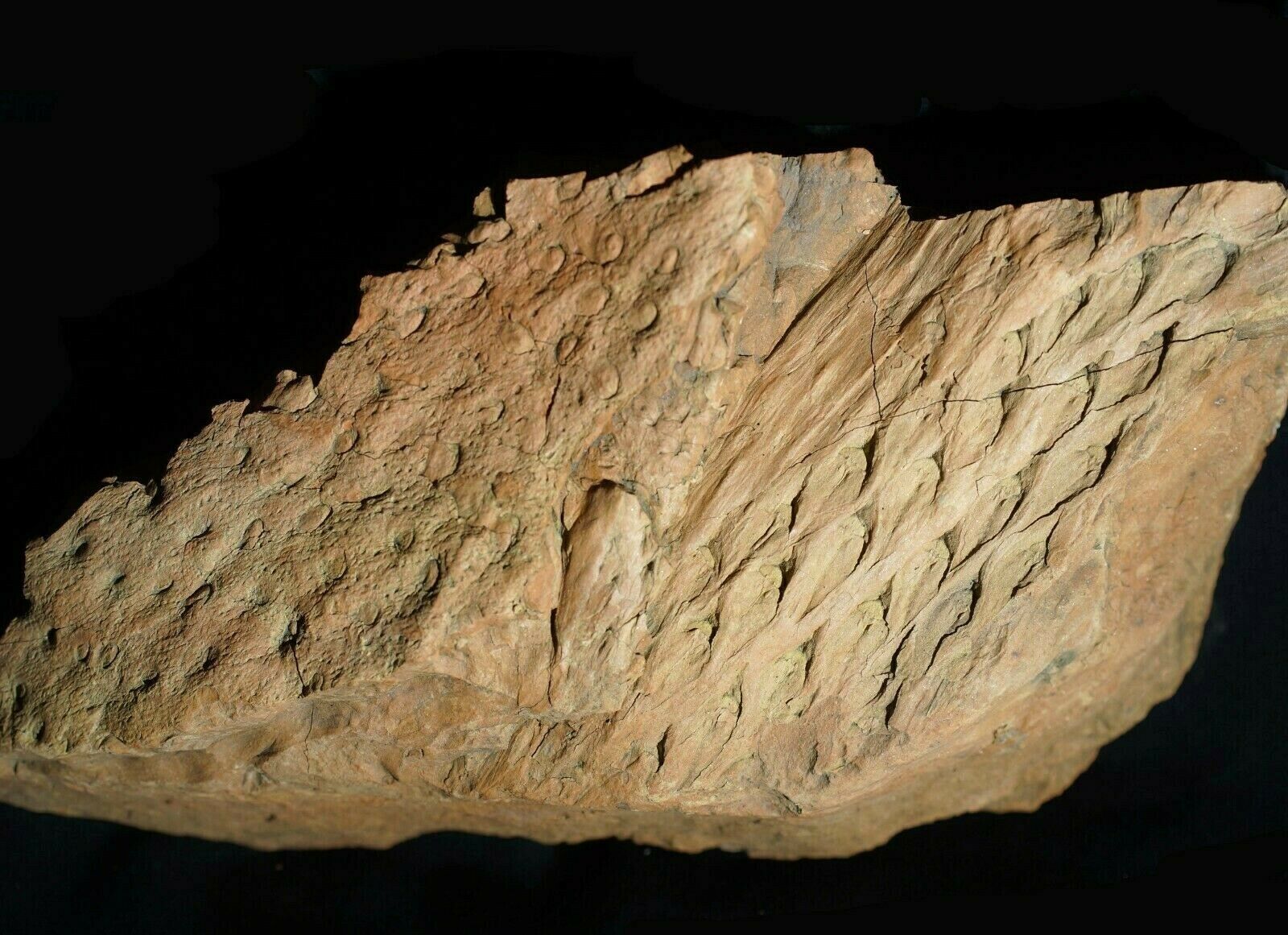
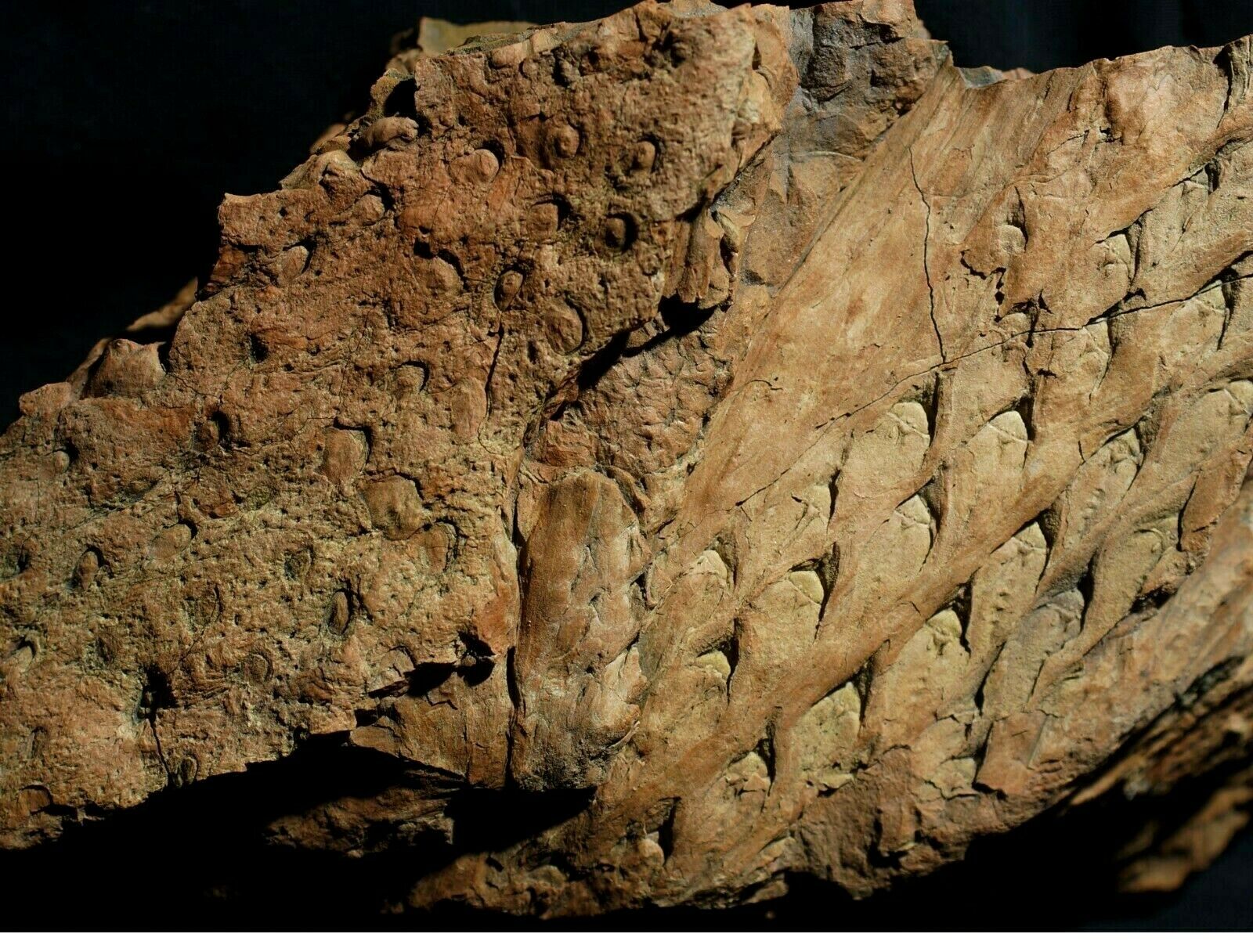
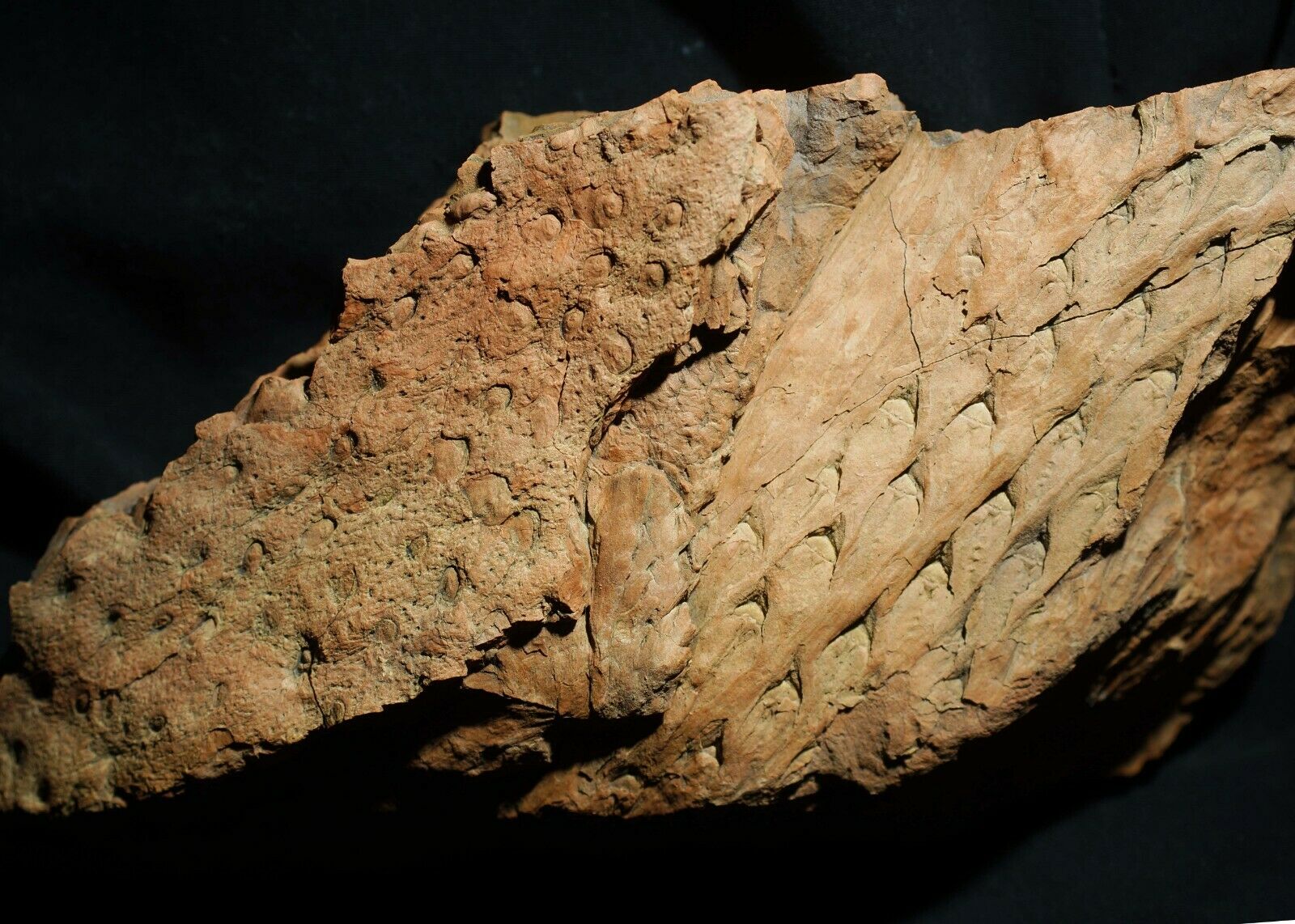
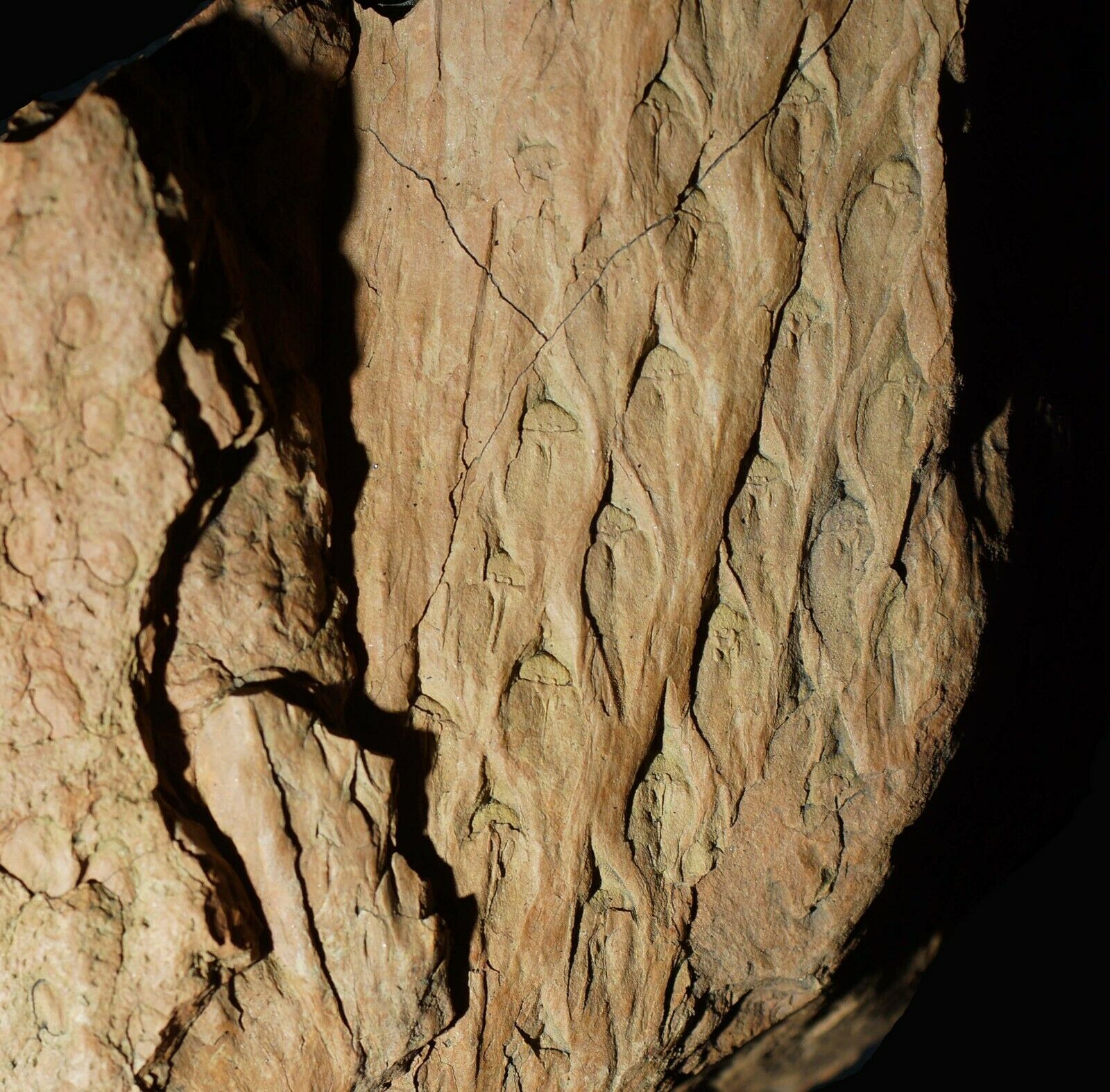
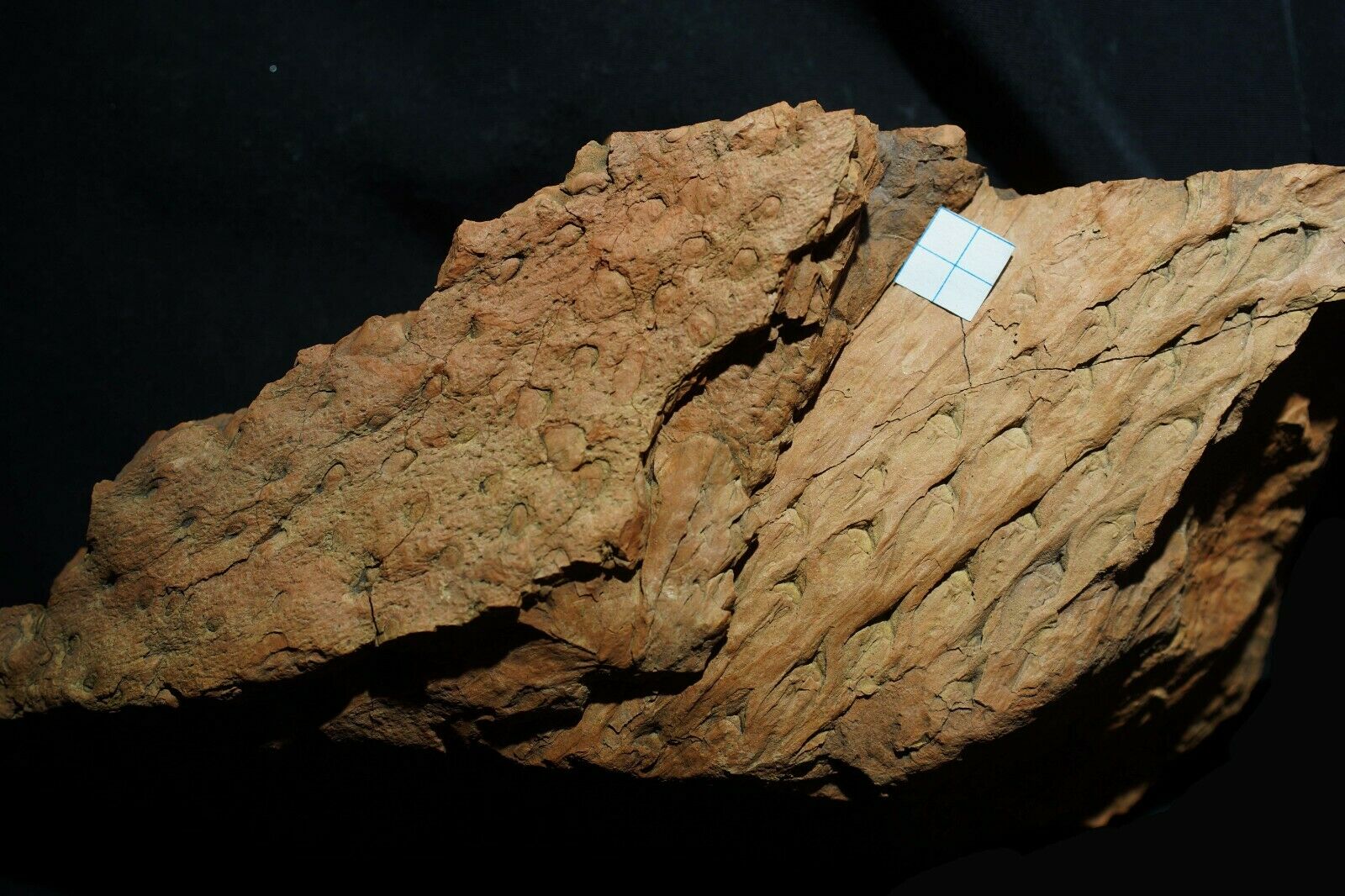
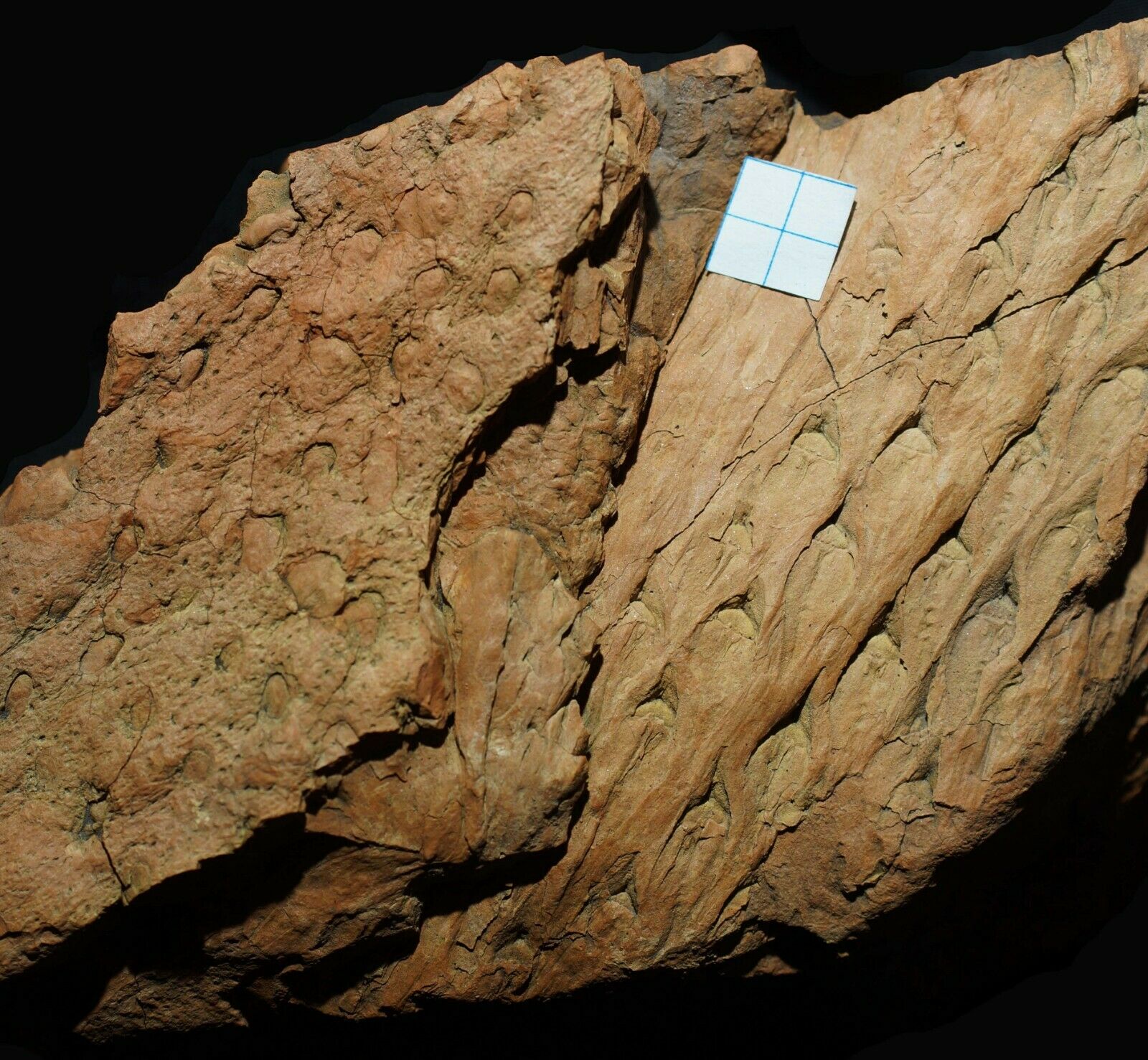
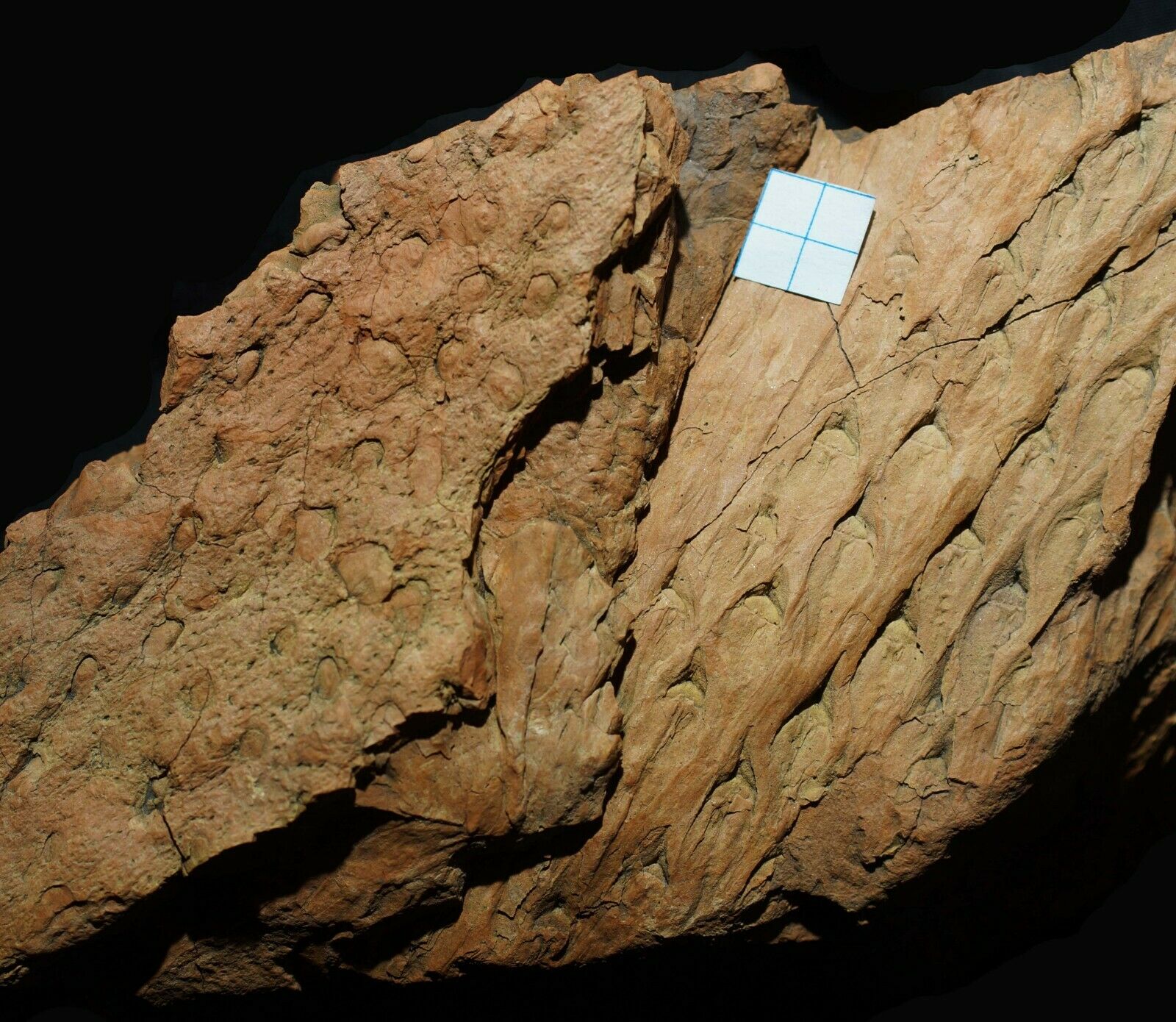
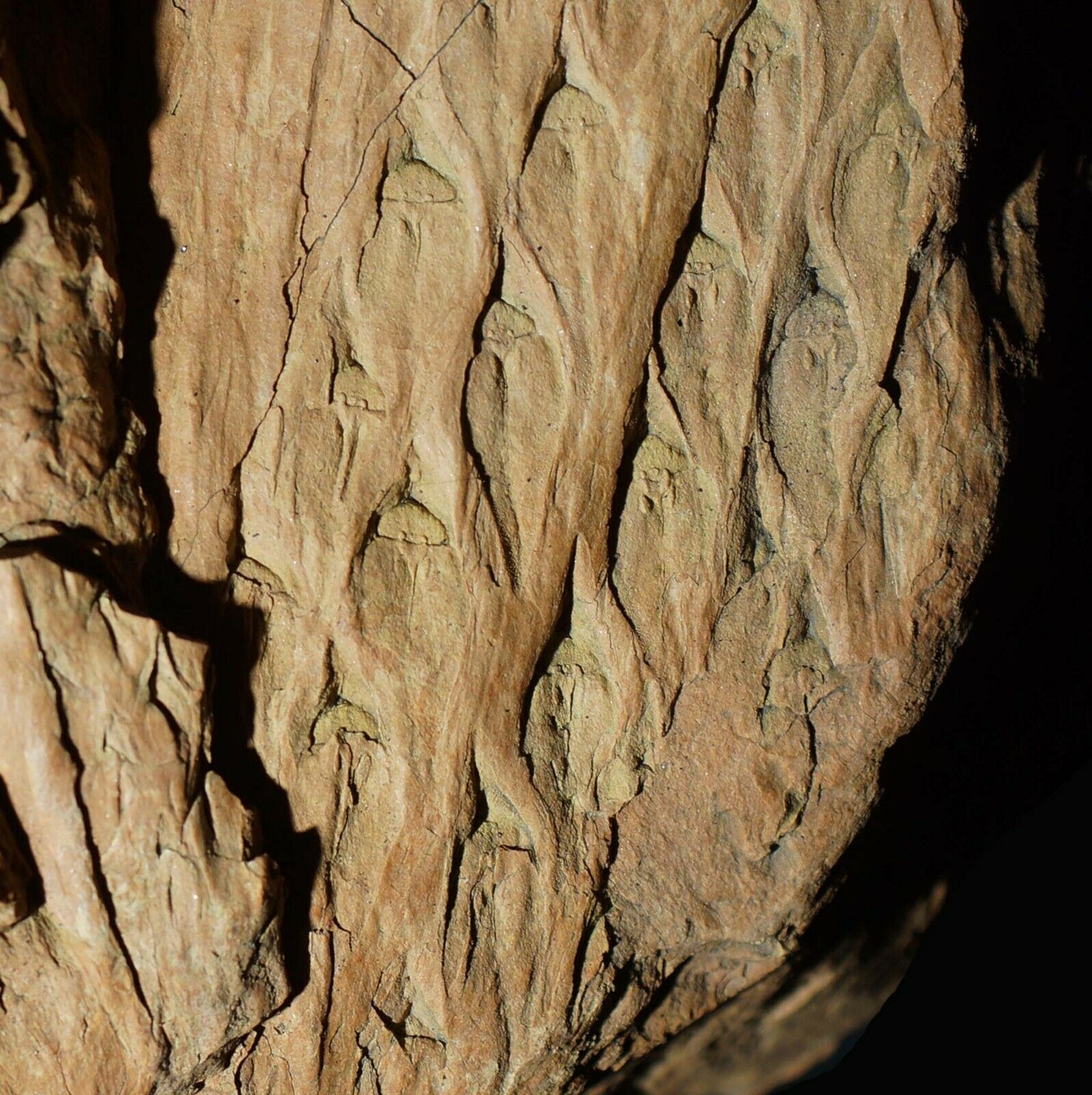
Beautiful, detailed specimen of
Lepidodendron aculeatum
STERNBERG &
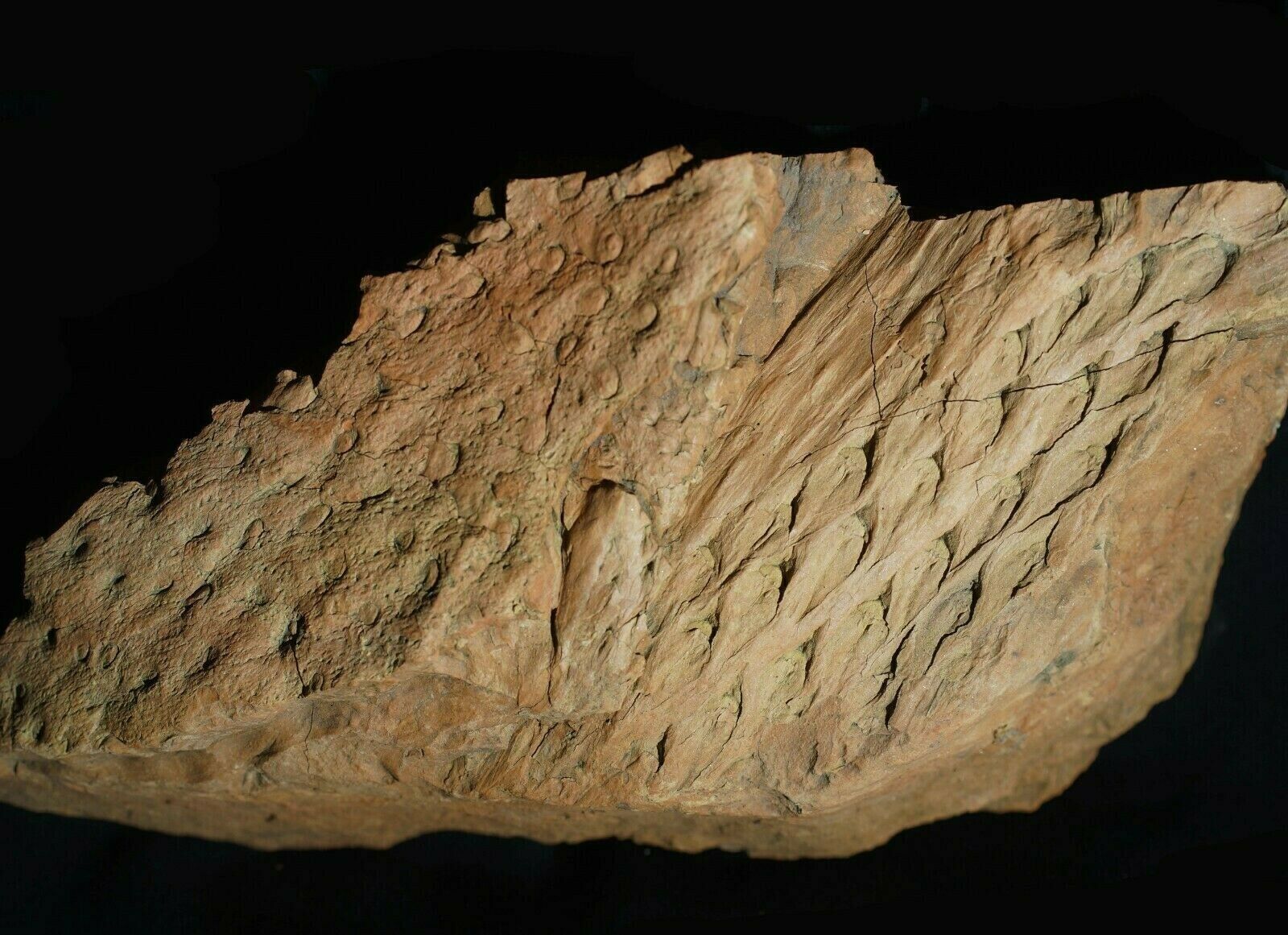
Stigmaria stellata
GOEPPERT
scale tree lycopod bark and roots !
Locality:
All detailed and accurate data will be provided with the specimen
Stratigraphy:
Upper Carboniferous¬† ‚Äď Mississippian -¬† Namurian A
Age:
ca. 326 Mya
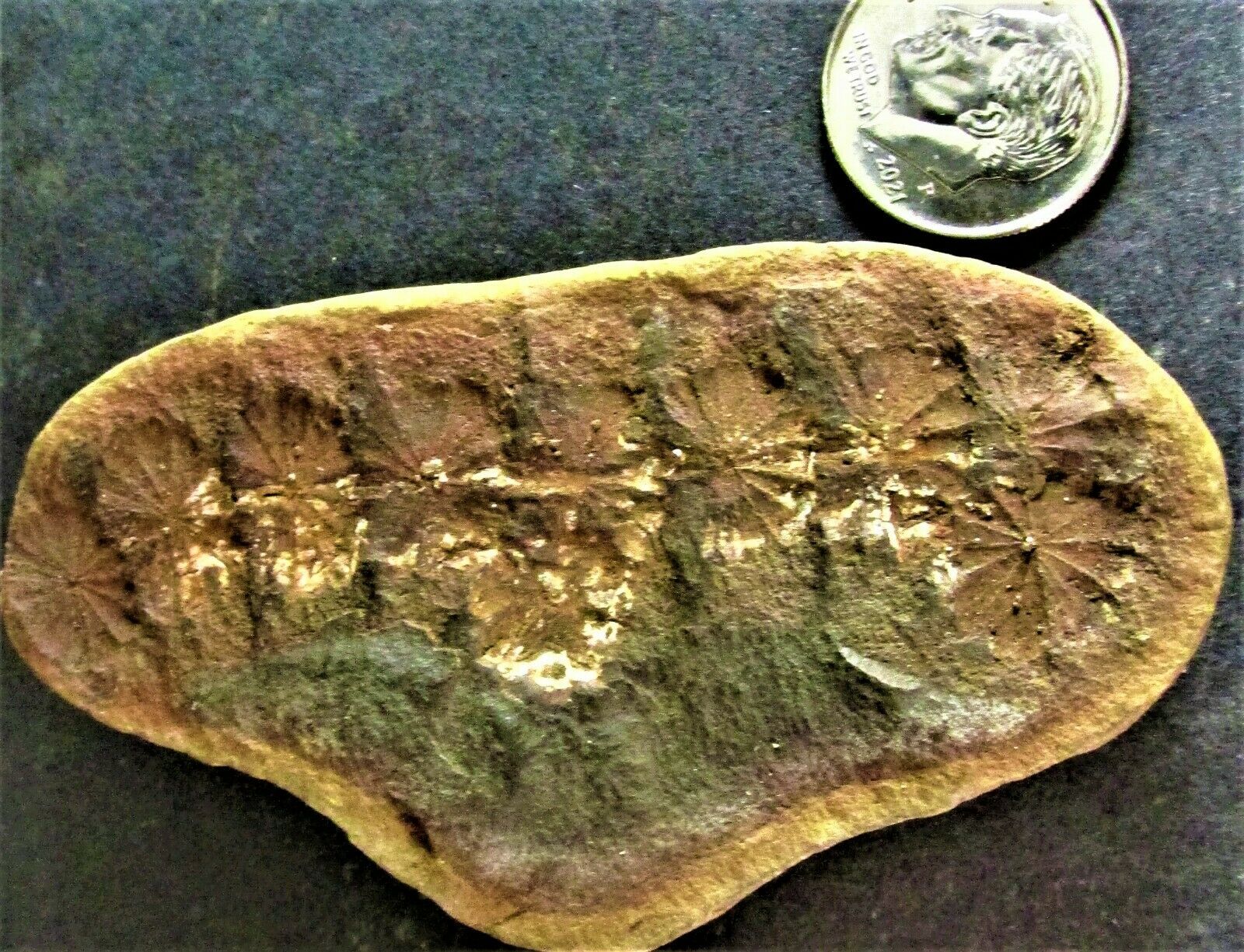
Matrix dimensions:
ca. 18,5 x 7,5 x 3,5 cm ( scale-bar - white square on pictures is 1,0 x 1,0 cm )
Description:
Beautiful, detailed specimen of
Lepidodendron aculeatum
STERNBERG &
Stigmaria stellata
GOEPPERT
scale tree lycopod bark and roots !
Lepidodendron
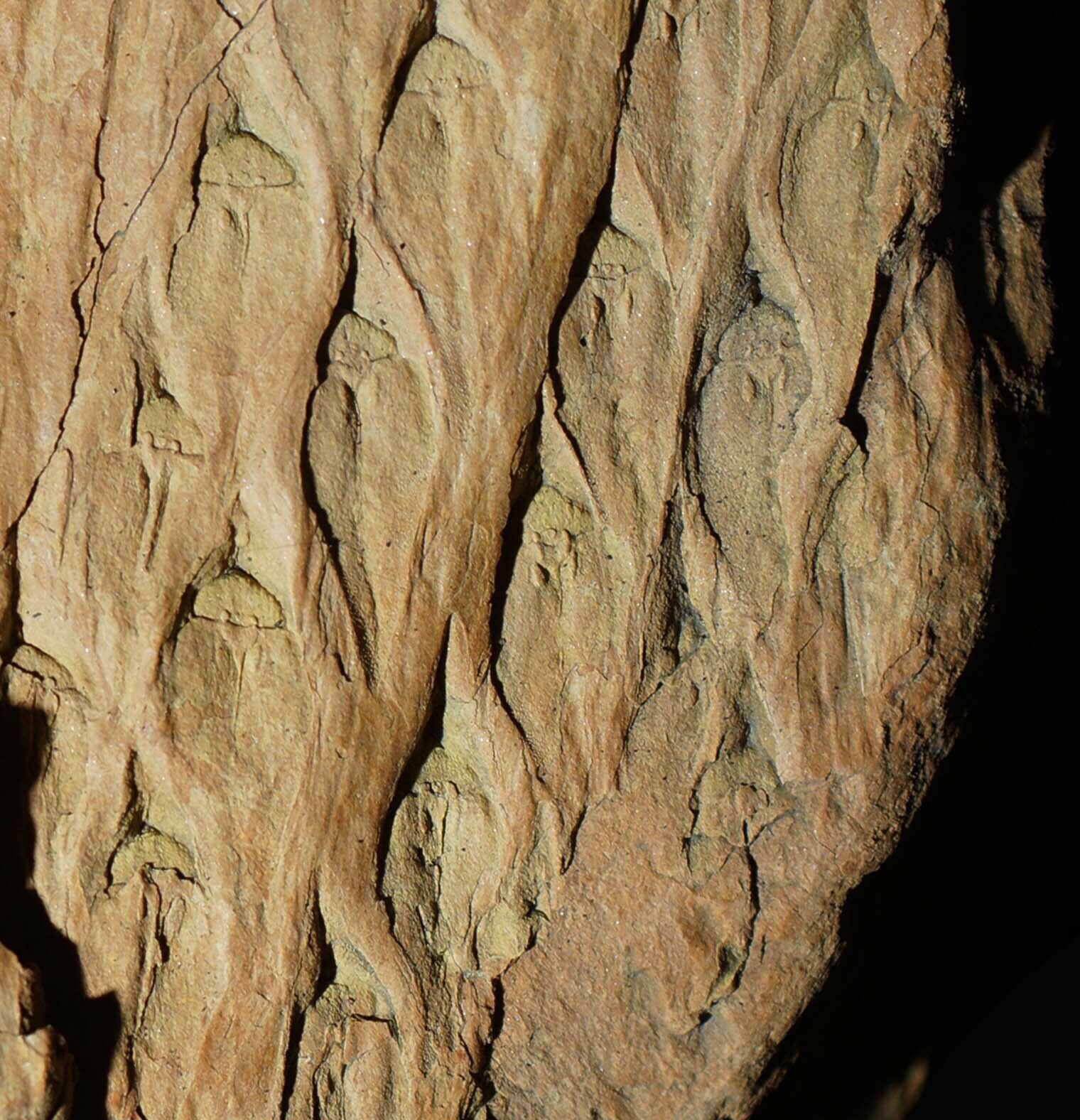
(also known as the "Scale tree") is an extinct genus of primitive, vascular, arborescent (tree-like) plant related to the Lycopsids (club mosses). It was part of the coal forest flora. They sometimes reached heights of over 30 metres (100 ft), and the trunks were often over 1 m (3.3 ft) in diameter, and thrived during the Carboniferous period. Sometimes called "giant club mosses", this is actually not correct as they are actually closer to quillworts than to club mosses. The closely packed diamond-shaped leaf scars left on the trunk and stems as the plant grew provide some of the most interesting and common fossils in Carboniferous shales and accompanying coal deposits. These fossils look much like tire tracks or alligator skin.
The scars, or leaf cushions, were composed of green photosynthetic tissue, evidenced by the cuticle covering and being dotted with stomata, microscopic pores through which carbon dioxide from the air diffuses into plants. Likewise, the trunks of
Lepidodendron
would have been green, unlike modern trees which have scaly, non-photosynthetic brown or gray bark.
Lepidodendron
has been likened to a giant herb. The trunks produced very little, if any, wood. Most structural support came from a thick, bark-like region. This region remained around the trunk as a rigid layer that did not flake off like that of most modern trees. As the tree grew, the leaf cushions expanded to accommodate the increasing width of the trunk.
The branches of this plant ended in cone-like structures.
Lepidodendron
did not produce seeds like many modern plants. Instead, it reproduced by means of spores. It is estimated that these plants grew rapidly and lived 10‚Äď15 years. Some species were probably monocarpic, meaning they reproduced only once toward the end of their life cycle.
Lepidodendron
likely lived in the wettest parts of the coal swamps that existed during the Carboniferous period. They grew in dense stands, likely having as many as 1000 to 2000 giant clubmosses per hectare. This would have been possible because they did not branch until fully grown, and would have spent much of their lives as unbranched poles. In its juvenile stages, the trunk was supported by grass-like leaves that grew straight out of the trunk. By the Mesozoic era, the giant clubmosses had died out and were replaced by smaller clubmosses, probably due to competition from the emerging woody gymnosperms and other plants.
Lepidodendron
is one of the more common plant fossils found in Pennsylvanian (Late Carboniferous) age rocks. They are closely related to other extinct genera,
Sigillaria
and
Lepidendropsis
.
In the 19th Century, due to the reptilian look of the diamond-shaped leaf scar pattern, petrified trunks of
Lepidodendron
were exhibited at fairgrounds as giant fossil lizards or snakes. The name
Lepidodendron
comes from the Greek
lepido
, scale, and
dendron
, tree.
Until now well understood are three species:
Stigmaria ficoides
,
Stigmaria rugulosa
and
Stigmaria reticulata
.
Stigmaria are a type of branching tree root fossil found in
Carboniferous
rocks. They were the roots of
coal forest lycopsid
trees such as
Sigillaria
and
Lepidodendron
.
Stigmaria
is the generic name given to fossil
root
casts
of various tree species of the Pennsylvanian Period, regardless of the form genera and species. The round nodes on the surface of
stigmaria
are scars where ribbon-like rootlets were once attached and arranged radially about
stigmaria
like the bristles of a bottle brush.
A flattened vascular tube is frequently visible on the end of
stigmaria
, located just off center of the axis of the root and running longitudinally down its length, which provided fluids  and perhaps nutrients to the main tree in life.
Systematic:
Division:          Tracheophyta (Lycoposida)
Class:              Lycopodinae
Order:              Lycophodiales
Family:            Lepidodendraceae
Genus:
Lepidodendron / Stigmaria
Species:
Lepidodendron aculeatum
STERNBERG /
Stigmaria stellata
GOEPPERT